NSS 4th
owo
依旧是赛后复现,主要是锻炼一下cuso的使用
Guillotine
1 | import random |
题目大意是给出了A,B,并且e∈(-3,3),并且我们一共有50组式子
1 | b = (sum(A[time][j][(secret >> j) & 1] for j in range(n))+e[time])%p |
提一嘴这里的(secret >> j) & 1指的就是secret的第j位(先把第j位挪到最右边,然后保留最后一位,其他位全部清零),然后我们根据这个比特选择 A[time][j][0] 或A[time][j][1]。对于这个选择我们仍然可以用数学式子来表示。
假设 x[j]∈{0,1},即 secret 的第 j 位。
那么:
如果 x[j]=0:
At[j][0]⋅(1−0)+At[j][1]⋅0=At[j][0]如果 x[j]=1x[j] = 1x[j]=1:
At[j][0]⋅(1−1)+At[j][1]⋅1=At[j][1]
所以这一项等价于:
At[j][(x[j])
然后我们就可以cuso一把梭(笑),大致讲一下cuso的用法,就是利用relations,bounds,modulus这三个已知量就能求对应的smallroots了
1 | from pwn import * |
LeetSpe4k
1 | from functools import reduce |
很有鸡块风格的代码。
看到h4sH就想到可能是fnv的题,这类题在去年ciscn,今年miniL和d3CTF好像都出现过。
那么直接就有这个式子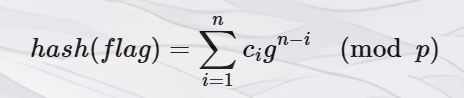
不过这里涉及到一个小技巧,学习了N1gh7ma12e师傅的博客[NSS 4th | N1gh7ma12e的小站](http://n1gh7ma12e.cn/2025/08/25/NSS 4th/)我们需要将“选择”看作一个式子。
比如把a替换成@可以写成(0,1,0,0)$*$(a,@,4,A)$^{T}$
这次咱就不用老办法,来试试科技,继续尝试cuso一把梭
1 | import cuso |
还是大概解释一下这个脚本
1 | var_groups = [] |
这一段的作用是构造方程的约束。
遍历 flag 模板里的字符:
- 如果是
{ } _ !,跳过(因为这些确定了)。 - 否则,找到它在
table里的对应分组,比如'a@4A'。 - 给这个字符创建一组 0/1 变量,如
x_5_0, x_5_1, x_5_2, x_5_3,代表在'a@4A'里选哪一个。 - 这些变量保证最终只会选一个候选字符
然后直接构造方程。最后通过解出来的一组变量赋值,找到哪个变量为1,从对应的table里选取字符,拼接得到完整的flag。
HiddenOracle
咕咕